MapReduce 论文阅读
MIT 6.824
Users specify a map function that processes a key/value pair to generate a set of intermediate key/value pairs, and a reduce function that merges all intermediate values associated with the same intermediate key.
Map接受用户输入然后产生一系列的键值对。
key1, key2, key3, key2MapReduce库将Map产生的键值对根据Key进行分组,然后传给Reduce。
key1:1, key2:1, key3:1, key2:1Reduce接受键值对,然后产生一个更小的键值对。
key1:1, key2:2, key3:1
MapReduce启发自Lisp的map和reduce。在Haskell中的对应示例为:
Prelude> map (+1) [1..10] [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11] Prelude> foldl (+) 0 [1..10] 55 Prelude>试图通过MapReduce这个库让没有分布式开发经验的程序员也能利用分布式集群的 性能。MapReduce这个库需要提程序员解决的问题包括但不限于:
分拆输入数据
任务调度和数据分发
管理机器间通信
容错性
负载均衡
etc…
流程概览
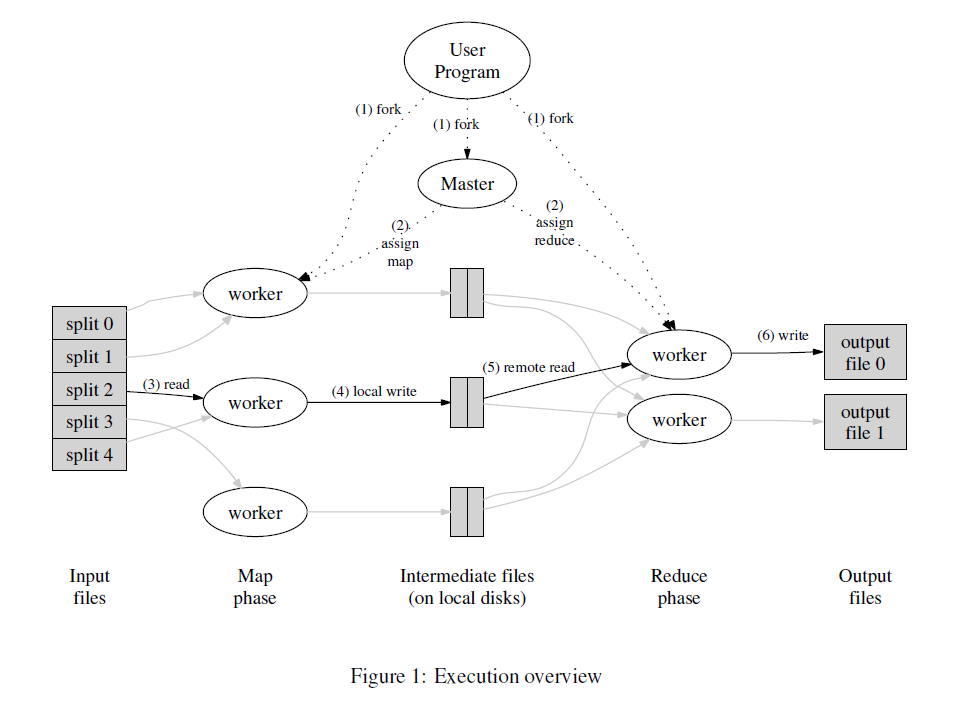
1. MapReduce先把数据分拆成16-64M之间的大小,然后fork自身,成为worker和master
2. master将会分配任务给worker们
3. 被分配执行map任务的程序读取被切割的文件块。调用用户的map函数,将其产生的
键值对存在内存里
4. 内存中的键值对会被持久化到硬盘上。然后将路径返回给master。
5. master将路径告知给执行reduce任务的程序,根据key将上一个环节的键值对排序
(因为数据量可能非常大以至于不能全部放在内存里)
6. 执行reduce任务的程序遍历排序后的键值对然后调用用户的reduce函数。将其返回值
追加到最终文件中。所以最终会产生n个输出文件,n为用户指定的reduce任务的数量。
7. 所有任务完成后,MapReduce返回,然后开始执行用户的其他代码。
容错性
worker failure: The master pings every worker periodically. If no response is received from a worker in a certain amount of time, the master marks the worker as failed. Any map task or reduce task in progress on a failed worker is also reset to idle and becomes eligible for rescheduling.
master failure: It is easy to make the master write periodic checkpoints of the master data structures described above. If the master task dies, a new copy can be started from the last checkpointed state.(不过此论文发布时 采用了简单的实现,即如果master失败,直接终止执行)
Lab
Part I: 正确实现
doMap和doReduce。根据figure1里的描述写代码,基本就不会错。 我在这里遇到的坑是没有仔细读论文,以为所有reduce函数公用一个输出文件。此处核心代码 为:// doMap for _, kv := range mapF(inFile, string(contents)) { i := ihash(kv.Key) % nReduce encs[i].Encode(&kv) } // doReduce mergeFileName := mergeName(jobName, reduceTaskNumber) mergeFile, err := os.Create(mergeFileName)Part II:统计单词。只要跟着描述来就行。仔细读一下给出的Hint和go的文档。
Part III:更改schedule.go。这里我花了点时间,因为大坑在于,我没想到在这一步 就要开始处理错误,还以为是在下一步呢,直到调试的时候看log,总是说没有reduce 的输出文件。然后果断给RPC调用加了个重试机制—死循环。然后就通过测试了。
for { if call(worker, "Worker.DoTask", doTaskArgs, nil) { wg.Done() break } }Part IV:处理worker出错。处理方式为如果worker失败,就把任务分配给其他worker执行, 所以也就是在上面的代码小改一下:
for { if call(worker, "Worker.DoTask", doTaskArgs, nil) { wg.Done() break } else { worker = <-registerChan } }Part V:统计单词出现的文件名。这个其实应该就是考是不是对MR真正的掌握了吧。 思路就是生成键值对的时候,单词为key,文件名为value然后进行MR。
总结:好玩儿!
 邮件 订阅
邮件 订阅
 RSS 订阅
RSS 订阅
 Web开发简介系列
Web开发简介系列
 数据结构的实际使用
数据结构的实际使用
 Golang 简明教程
Golang 简明教程
 Python 教程
Python 教程