httprouter源码阅读与分析
httprouter是Go里比较高效的一个http 路由框架,比如GIN就是基于它。我们来看看httprouter的源码。
首先要明确的一点是httprouter基于radix tree这种数据结构:
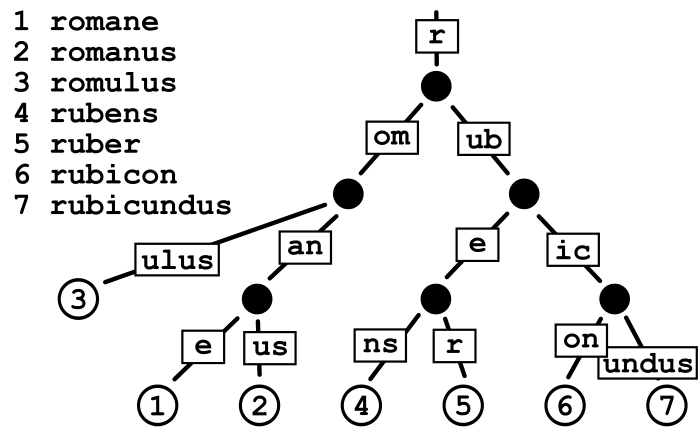
按照管理,我们先来看看demo,然后从demo跟进代码实现:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"log"
"github.com/julienschmidt/httprouter"
)
func Index(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, _ httprouter.Params) {
fmt.Fprint(w, "Welcome!\n")
}
func Hello(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, ps httprouter.Params) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "hello, %s!\n", ps.ByName("name"))
}
func main() {
router := httprouter.New()
router.GET("/", Index)
router.GET("/hello/:name", Hello)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", router))
}
首先看到 httprouter.New(),因为它返回一个router实例:
func New() *Router {
return &Router{
RedirectTrailingSlash: true,
RedirectFixedPath: true,
HandleMethodNotAllowed: true,
HandleOPTIONS: true,
}
}
// Router is a http.Handler which can be used to dispatch requests to different
// handler functions via configurable routes
type Router struct {
trees map[string]*node
paramsPool sync.Pool
maxParams uint16
SaveMatchedRoutePath bool
RedirectTrailingSlash bool
RedirectFixedPath bool
HandleMethodNotAllowed bool
HandleOPTIONS bool
GlobalOPTIONS http.Handler
globalAllowed string
NotFound http.Handler
MethodNotAllowed http.Handler
PanicHandler func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request, interface{})
}
它实现了 ServeHTTP 这个函数,因此符合 net/http.Handler 接口:
// ServeHTTP makes the router implement the http.Handler interface.
func (r *Router) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
if r.PanicHandler != nil {
defer r.recv(w, req)
}
path := req.URL.Path
if root := r.trees[req.Method]; root != nil {
if handle, ps, tsr := root.getValue(path, r.getParams); handle != nil {
if ps != nil {
handle(w, req, *ps)
r.putParams(ps)
} else {
handle(w, req, nil)
}
return
...
}
这就是处理请求的时候,查找路由树及handler的那部分,root.getValue就是查找路由树的具体函数,不过细节此处不表。
我们接下来看看注册路由的那部分:
// GET is a shortcut for router.Handle(http.MethodGet, path, handle)
func (r *Router) GET(path string, handle Handle) {
r.Handle(http.MethodGet, path, handle)
}
// 跟进 r.Handle 函数之后发现调用了 addRoute 函数
// addRoute adds a node with the given handle to the path.
// Not concurrency-safe!
func (n *node) addRoute(path string, handle Handle) {
fullPath := path
n.priority++
// Empty tree
if len(n.path) == 0 && len(n.indices) == 0 {
n.insertChild(path, fullPath, handle)
n.nType = root
return
}
walk:
for {
...
}
而 addRoute 函数就是实现radix tree这个数据结构的函数了,它会先找到共同的部分,然后考虑是否把路由切分为字节点,最后
把handler写上去(调用 insertChild 函数)。
type node struct {
path string // URL
indices string // 字节点的首字母拼成的string,顺序与 children 一致
wildChild bool // 是否是泛匹配
nType nodeType // 节点类型
priority uint32 // 优先级
children []*node // 子节点
handle Handle // 处理函数
}
node就是保存这些资料的radix tree的节点。
参考资料:
 邮件 订阅
邮件 订阅
 RSS 订阅
RSS 订阅
 Web开发简介系列
Web开发简介系列
 数据结构的实际使用
数据结构的实际使用
 Golang 简明教程
Golang 简明教程
 Python 教程
Python 教程